Abstract
This paper presents a time series prediction using radial basis function (RBF) network with the affine transformation of training data. Conventionally, the training data for time series prediction is considered in the absolute coordinate system, and these results in the poor prediction. For highly accurate time series prediction, in this paper, the affine transformation is applied to the training data. Therefore, the training data are transformed into the rotated coordinate system using the affine transformation, and the time series prediction using the RBF network is made in this coordinate system. The proposed approach is simple and easy to implement. Several benchmarks are selected to examine the proposed approach, and the root mean square error (RMSE) is used to numerically evaluate the prediction accuracy. It is found from the numerical results that the highly accurate prediction can be made by the proposed approach, in comparison with the conventional RBF network.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Casdagli, M., Nonlinear prediction if chaotic time series, Phys. D (Amsterdam, Neth.), 1998, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 335–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2789(89)90074-2
Zhang, W. and Wei, D., Prediction for network traffic of radial basis function neural network model based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm, Neural Comput. Appl., 2018, vol. 29, pp. 1143–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2483-5
Cao, L., Support vector machines experts for time series forecasting, Neurocomputing, 2003, vol. 51, pp. 321–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-2312(02)00577-5
Luo, C., Huang, C., Cao, J., Lu, J., Huang, W., Guo, J., and Wei, Y., Short-term traffic flow prediction based on least square support vector machine with hybrid optimization algorithm, Neural Process. Lett., 2019, vol. 50, pp. 2305–2322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-019-09994-8
Cowper, M.R., Mulgrew, B., and Unsworth, C.P., Nonlinear prediction of chaotic signals using a normalised radial basis function network, Signal Process., 2002, vol. 82, pp. 775–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-1684(02)00155-X
Harpham, C. and Dawson, C.W., The effect of different basis functions on a radial basis function network for time series prediction: A comparative study, Neurocomputing, 2006, vol. 69, nos. 16–18, pp. 2161–2170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2005.07.010
Du, H. and Zhang, N., Time series prediction using evolving radial basis function networks with new encoding scheme, Neurocomputing, 2008, vol. 71, pp. 1388–1400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2007.06.004
Gan, M., Peng, H., and Dong, X., A hybrid algorithm to optimize RBF network architecture and parameters for nonlinear time series prediction, Appl. Math. Modell., 2012, vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 2911–2919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2011.09.066
Markopoulos, A.P., Georgiopoulos, S., and Manolakos, D.E., On the use of back propagation and radial basis function neural networks in surface roughness prediction, J. Ind. Eng. Int., 2016, vol. 12, pp. 389–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40092-016-0146-x
Manjunatha, R., Narayana, P.B., Reddy, K.H., and Reddy, V.K., Radial basis function neural networks in prediction and modeling of diesel engine emissions operated for biodiesel blends under varying operating conditions, Indian J. Sci. Technol., 2012, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 2307–2312. https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2012/v5i3.14
He, X. and Lapedes, A., Nonlinear modeling and prediction by successive approximation using radial basis functions, Phys. D (Amsterdam, Neth.), 1994, vol. 70, no. 3, pp. 289–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2789(94)90018-3
Hong, W.-C., Dong, Y., Zheng, F., and Wei, S.Y., Hybrid evolutionary algorithms in a SVR traffic flow forecasting model, Appl. Math. Comput., 2011, vol. 217, no. 15, pp. 6733–6747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2011.01.073
Hu, W., Yan, L., Liu, K., and Wang, H., A short-term traffic flow forecasting method based on the hybrid PSO-SVR, Neural Process. Lett., 2016, vol. 43, pp. 155–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-015-9409-6
Luo, C., Huang, C., Cao, J., Lu, J., Huang, W., Guo, J., and Wei, Y., Short-term traffic flow prediction based on least square support vector machine with hybrid optimization algorithm, Neural Process. Lett., 2019, vol. 50, pp. 2305–2322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-019-09994-8
Nakayama, H., Arakawa, M., and Sasaki, R., Simulation-based optimization using computational intelligence, Optim. Eng., 2002, vol. 3, pp. 201–214. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020971504868
Kitayama, S. and Yamazaki, K., Simple estimate of the width in Gaussian kernel with adaptive scaling technique, Appl. Soft Comput., 2011, vol. 11, pp. 4726–4737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2011.07.011
Kitayama, S., Yokoyama, M., Kawamoto, K., Noda, T., Miyasaka, T., and Echigo, Y., Practical approach of simultaneous optimization of variable blank holder force and variable slide velocity trajectory in sheet metal forming, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, vol. 98, pp. 2693–2703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2411-1
Kitayama, S., Ishizuki, R., Takano, M., Kubo, Y., and Aiba, S., Optimization of mold temperature profile and process parameters for weld line reduction and short cycle time in rapid heat cycle molding, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, vol. 103, pp. 1735–1744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03685-3
Kitayama, S., Saikyo, M., Nishio, Y., and Tsutsumi, K., Torque control strategy and optimization for fuel consumption and emission reduction in parallel hybrid electric vehicles, Struct. Multidiscip. Optim., 2015, vol. 52, pp. 595–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1254-8
András, P., The equivalence of support vector machine and regularization neural networks, Neural Process. Lett., 2002, vol. 15, pp. 97–104. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015292818897
Kitayama, S. and Yamazaki, K., Simple estimate of the width in Gaussian kernel with adaptive scaling technique, Appl. Soft. Comput., 2011, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 4726–4737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2011.07.011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
The proposed approach is applied to the following two driving cycles, and the results are summarized. Like Section 4.2, the vehicle speed is predicted by using the torque and the engine speed, and the RMSE is used to evaluate the accuracy of prediction.
Worldwide harmonized Light duty driving Test Cycle (WLTC), which is a current standard driving cycle for fuel consumption.
Los Angeles number 4 mode (LA4), in which the driving in urban area is assumed.
Each driving cycle is shown in Fig. A1, and the characteristics are summarized in Table A1.
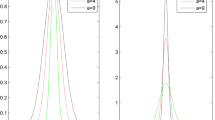
It is difficult to compare the prediction result through the driving cycle, and two parts are selected for the comparison. The results are then shown in Fig. A2 with the enlarged view and the RMSE is also listed in Table A2. Note that the white dots in Fig. A2 denote the predicted points. It is found from Fig. A2 and Table A2 that highly accurate time series prediction can be made by the proposed RBF.
About this article
Cite this article
Satoshi Kitayama, Kohei Saito Time Series Prediction Using Radial Basis Function Network with Transformation of Training Data and Its Applications. Aut. Control Comp. Sci. 56, 239–252 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411622030026
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411622030026