Abstract
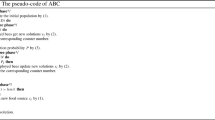
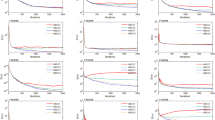
Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm is widely used in optimization problems due to its few parameters and simple structure. However, there are shortcomings such as relatively slow convergence and easy to optimize stagnation. This paper proposes an artificial bee colony algorithm based on slime mold and marine predators (SMA-MPA-ABC) to overcome the insufficiency of ABC algorithm. The slime mold foraging strategy is introduced into the neighborhood search process of employed bees. The employed bee generates positive feedback and negative feedback according to the size of the food concentration, generates adaptive weights, and adjusts the search mode to search in the direction of the optimal solution to speed up the convergence speed. In addition, the fish gathering device effect in the marine predator algorithm is introduced in the scout bee phase to avoid optimization stagnation. The simulation experiment results of 15 benchmark test functions show that SMA-MPA-ABC algorithm has a faster convergence speed, higher convergence accuracy, and better stability than the ABC algorithm and other improved ABC algorithms.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Karaboga, D., An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization, Technical Report-Tr06, Kayseri, Turkey: Erciyes Univ., 2005.
Karaboga, D. and Basturk, B., On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm, Appl. Soft Comput., 2007, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 687–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2007.05.007
Ogren, R.M. and Kong, S.C., Optimization of diesel fuel injection strategies through applications of cooperative particle swarm optimization and artificial bee colony algorithms, Int. J. Engine Res., 2021, vol. 22, no. 9, pp. 3030–3041. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468087420954020
Xu, Y. and Wang, X.L., An artificial bee colony algorithm for scheduling call centres with weekend-off fairness, Appl. Soft Comput., 2021, vol. 109, p. 107542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107542
Bayraktar, T., Ersöz, F., and Kubat, C., Effects of memory and genetic operators on artificial bee colony algorithm for single container loading problem, Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 108, p. 107462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107462
Li, S.M., Chen, H.L., Wang, M.J., Heidari, A.A., and Mirjalili, S., Slime mould algorithm: a new method for stochastic optimization, Future Gener. Comput. Syst., 2020, vol. 111, pp. 300–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.03.055
Faramarzi, A., Heidarinejad, M., Mirjalili, S., and Gandomi, A.H., Marine predators algorithm: a nature-inspired metaheuristic, Expert Syst. Appl., 2020, vol. 152, p. 113377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113377
Zhang, M., Tan, Y.T., Zhu, J., Chen, Y.N., and Liu, H.M., Modeling and simulation of improved artificial bee colony algorithm with data-driven optimization, Simul. Model. Pract. Theory, 2019, vol. 93, pp. 305–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2018.06.004
Bai, W., Eke, I., and Lee, K.Y., An improved artificial bee colony optimization algorithm based on orthogonal learning for optimal power flow problem, Control Eng. Pract., 2017, vol. 61, pp. 163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2017.02.010
Taetragool, U., Sirinaovakul, B., and Achalakul, T., NeSS: A modified artificial bee colony approach based on nest site selection behavior, Appl. Soft Comput., 2018, vol. 71, pp. 659–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.048
Bajer, D. and Zorić, B., An effective refined artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical optimisation, Inf. Sci., 2019, vol. 504, pp. 221–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.07.022
Sharma, N., Sharma, H., and Sharma, A., Beer froth artificial bee colony algorithm for job-shop scheduling problem, Appl. Soft Comput., 2018, vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 507–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.04.001
Xiang, W.L., Li, Y.Z., Meng, X.L., Zhang, C.M., and An, M.Q., A grey artificial bee colony algorithm, Appl. Soft Comput., 2017, vol. 60, pp. 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.06.015
Xiang, W.L. and An, M.Q., An efficient and robust artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical optimization, Comput. Oper. Res., 2013, vol. 40, no. 5, pp. 1256–1265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2012.12.006
Wang, H., Wang, W.J., Xiao, S.Y., Cui, Z.H., Xu, M.Y., and Zhou, X.Y., Improving artificial bee colony algorithm using a new neighborhood selection mechanism, Inf. Sci., 2020, vol. 527, pp. 227–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.03.064
Abdel-Basset, M., Chang, V., and Mohamed, R., HSMA_WOA: A hybrid novel slime mould algorithm with whale optimization algorithm for tackling the image segmentation problem of chest x-ray images, Appl. Soft Comput., 2020, vol. 95, p. 106642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106642
Rizk-Allah, R.M., Hassanien, A.E., and Song, D., Chaos-opposition-enhanced slime mould algorithm for minimizing the cost of energy for the wind turbines on high-altitude sites, ISA Trans., 2021, vol. 121, pp. 191–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2021.04.011
Hassan, M.H., Kamel, S., Abualigah, L., and Eid, A., Development and application of slime mould algorithm for optimal economic emission dispatch, Expert Syst. Appl., 2021, vol. 128, p. 115205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115205
Mohamed, A.B., Mohamed, R., Elhoseny, M., Bashir, A.K., and Kumar, N., Energy-aware marine predators algorithm for task scheduling in IoT-based fog computing applications, IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf., 2020, vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 5068–5076. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2020.3001067
Houssein, E.H., Mohamed, M., Ahmed, F., Hegazy, R., and Kumar, N., A modified marine predator algorithm based on opposition based learning for tracking the global MPP of shaded PV system, Expert Syst. Appl., 2021, vol. 183, p. 115253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115253
Ho, L.V., Nguyen, D.H., Mousavi, M., De, R.G., Bui, T.T., Gandomi, A.H., and Wahab, M.A., A hybrid computational intelligence approach for structural damage detection using marine predator algorithm and feedforward neural networks, Comput. Struct., 2021, vol. 252, p. 106568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2021.106568
Panagant, N., Yıldız, M., Pholdee, N., Yıldız, A.R., Bureerat, S., and Sait, S.M., A novel hybrid marine predators-nelder-mead optimization algorithm for the optimal design of engineering problems, Mater. Test, 2021, vol. 63, no. 5, pp. 453–457. https://doi.org/10.1515/mt-2020-0077
Filmalter, J.D., Dagorn, L., Cowley, P.D., and Taquet, M., First descriptions of the behavior of silky sharks, Carcharhinus falciformis, around drifting fish aggregating devices in the Indian Ocean, Bull. Mar. Sci., 2011, vol. 87, no. 3, pp. 325–337. https://doi.org/10.5343/bms.2010.1057
Wolpert, D.H. and Macready, W.G., No free lunch theorems for optimization, IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput., 1997, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 67–82. https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.585893
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Liyi Zhang, Tang, J., Liu, T. et al. An Improved Artificial Bee Colony Optimization Algorithm Based on Slime Mold and Marine Predator. Aut. Control Comp. Sci. 56, 481–493 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411622060116
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0146411622060116